Abstract
Background: In AML, leukemic transformation causes clonal expansion of immature cells through de-regulated cell division cycles. CDK4/CDK6 regulates neoplastic progression, which might represent an effective strategy for treating AML. But current clinical data shows either limited efficacy or elusive results. Bromodomain and extra-terminal (BET) inhibitors interferes with transcriptional complexes and disrupting gene transcription of key oncogenes such as MYC. Also, there is need to explore usage of other receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Therefore, a drug combination strategy should be explored to overcome limited clinical efficacy.
Aims: To create digital drug models for BET inhibition (BETi), CDK4/6 inhibition (CDKi), FLT3 inhibition (FLT3i) and validate the predicted responses in AML patient samples with ex vivo chemosensitivity testing. Furthermore, to validate the identified combination of BET inhibitor with CDK4/6 inhibitor or FLT3 inhibitor.
Methods: The Beat AML project (supported by the Leukemia & Lymphoma Society) collects clinical data and bone marrow specimens from AML patients. Bone marrow samples are analyzed by conventional cytogenetics, whole-exome sequencing, RNAseq, and an ex vivo chemosensitivity assay. 33 patients were randomly chosen. Every available genomic abnormality was inputted into a computational biology model (CBM, Cell Works Group Inc.) that uses PubMed and other online resources to generate patient-specific protein network maps of activated and inactivated pathways. Digital drug simulations with BETi (JQ1), CDKi (palbociclib), FLT3i (sorafenib) were conducted by quantitatively measuring drug effect on a composite AML disease inhibition score (i.e., cell proliferation, viability, and apoptosis). Paired comparisons between the computational predictions and the sample's ex vivo chemosensitivity IC50 values were conducted.
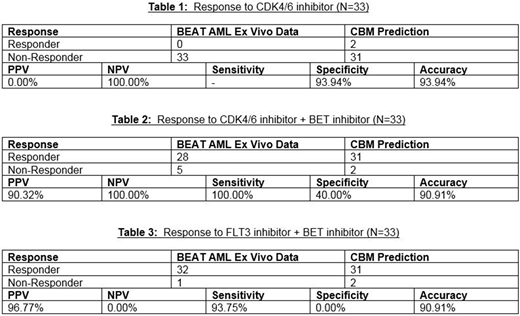
Results: None of the 33 AML patients showed ex vivo chemosensitivity to palbociclib alone, and the CBM method was highly accurate (94%) in predicting this lack of response (Table 1). Through CBM mapping the following genetic mutations were identified as potentially contributing to palbociclib resistance: loss of function (LOF) of RB1 (Retinoblastoma 1), LOF of PTCH1 (patched 1), LOF of FBXW7 (F-box and WD repeat domain containing 7), gain of function (GOF) of CCNE1/2 (Cyclin E1/2) or LOF in NPM1 (nucleophosmin 1). Additionally, the CBM method showed that NPM1 mutated AML cases that were resistant to palbociclib also showed a better response to the combination of palbociclib and JQ1. In 28/33 (85%) patients, this combination of palbociclib and BETi (JQ1) was toxic to AML cells in ex vivo chemosensitivity assay (Table 2). The CBM method predicted that 31/33 (94%) of AML patients would respond to palbociclib and JQ1 (Table 2), and the accuracy of matching between CBM and ex vivo chemosensitivity assay was 91% (Table 2). Another combination with high proportion of responding patients was FLT3i and BETi (Table 3), with accuracy of matching between CBM and ex vivo assay of 91% (Table 3). Furthermore, computational analysis of the combination of BETi and FLT3i revealed that patients with mutation of NPM1 along with FLT3 TKD/ITD mutation showed high degree of synergy at lower drug concentrations.
Conclusion: Digital drug simulations of inhibitions of CDK4/6, BET, and FLT3 using AML patient genomic data accurately matched ex vivo chemosensitivity results. The integration of computational biology modeling and Beat AML data led to the identification of potential palbociclib resistance pathways in AML, which led to the rational design of new multi-drug regimens. This integrated system enabled novel inferences that informs future clinical trials for patients with AML.
Tyner:Janssen: Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding; Takeda: Research Funding; Leap Oncology: Equity Ownership; Gilead: Research Funding; Syros: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Research Funding; Agios: Research Funding; Aptose: Research Funding; AstraZeneca: Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding. Druker:Cepheid: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; GRAIL: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Blueprint Medicines: Consultancy, Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Vivid Biosciences: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Beta Cat: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Millipore: Patents & Royalties; MolecularMD: Consultancy, Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; ALLCRON: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Aptose Therapeutics: Consultancy, Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Gilead Sciences: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Aileron Therapeutics: Consultancy; Patient True Talk: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy; Amgen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; McGraw Hill: Patents & Royalties; Bristol-Meyers Squibb: Research Funding; Third Coast Therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Henry Stewart Talks: Patents & Royalties; Oregon Health & Science University: Patents & Royalties; Leukemia & Lymphoma Society: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Novartis Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; Monojul: Consultancy; ARIAD: Research Funding; Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center: Research Funding. Vidva:Cellworks Research India Private Limited: Employment. Narvekar:Cellworks Research India Private Limited: Employment. Agrawal:Cellworks Research India Private Limited: Employment. Gera:Cellworks Research India Private Limited: Employment. Prasad:Cellworks Research India Private Limited: Employment. Shyamasundar:Cellworks Research India Private Limited: Employment. Tunwer:Cellworks Research India Private Limited: Employment. Abbasi:Cell Works Group Inc.: Employment. Vali:Cell Works Group Inc.: Employment. Cogle:Celgene: Other: Steering Committee Member of Connect MDS/AML Registry.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal